STM32CubeIDE Integration Guide
The following guide will walk you through step-by-step how to integrate and test the Memfault SDK for a STM32 device using STM32CubeIDE.
1. Create a Project
Create a Project and get a Project Key
Go to app.memfault.com and from the "Select A Project" dropdown, click on "Create Project" to setup your first project. Choose a name that reflects your product, such as "smart-sink-dev".
Once you've created your project, you'll be automatically taken to an page that includes your project key. Copy the key and follow the rest of this guide.
2. Set up the SDK
The following steps will be walking through adding Memfault to a standard
STM32CubeIDE example project. For reference, this project is located at
~/STM32CubeIDE/workspace_1.16.1/Virtual_COM_Port with the following directory
structure:
.
├── .git
├── .gitignore
├── .mxproject
├── Binary
├── Drivers
├── Inc
├── Middlewares
├── README.md
├── STM32CubeIDE
├── Src
├── Virtual_COM_Port.ioc
└── readme.html
Add Memfault SDK as a Submodule
Add SDK as a submodule at top level of project (i.e. project folder within the workspace):
cd $PROJECT_ROOT # e.g. ~/STM32CubeIDE/workspace_1.16.1/Virtual_COM_Port
git submodule add https://github.com/memfault/memfault-firmware-sdk.git memfault-firmware-sdk
git add . # stage the addition of the submodule
Your directory structure should now look like:
.
├── .git
├── .gitignore
├── .gitmodules # <-- new
├── .mxproject
├── Binary
├── Drivers
├── Inc
├── Middlewares
├── README.md
├── STM32CubeIDE
├── Src
├── Virtual_COM_Port.ioc
├── memfault-firmware-sdk # <-- new
└── readme.html
Note that because the SDK is intentionally not nested into the STM32CubeIDE folder, Memfault sources will not get picked up by the build by default. In the next step, we will add these sources to the STM32CubeIDE build system.
Link Memfault Includes and Sources to STM32CubeIDE Build System
Next, use the Memfault Eclipse project patcher script to link Memfault includes and sources into the project using these arguments:
--memfault-sdk-dir: The directorymemfault-firmware-sdkwas copied to--project-dir: The directory with the Eclipse.projectto update
cd $PROJECT_ROOT # e.g. ~/STM32CubeIDE/workspace_1.16.1/Virtual_COM_Port
python3 memfault-firmware-sdk/scripts/eclipse_patch.py \
--memfault-sdk-dir memfault-firmware-sdk \
--project-dir STM32CubeIDE
Writing result to ~/STM32CubeIDE/workspace_1.16.1/Virtual_COM_Port/STM32CubeIDE/.project
Writing result to ~/STM32CubeIDE/workspace_1.16.1/Virtual_COM_Port/STM32CubeIDE/.cproject
Hurray, .project & .cproject have been successfully patched! Be sure to 'Refresh' project to synchronize changes!
As noted in the message, run a Refresh on the project to ensure STMCubeIDE
picks up the changes. Your directory structure in STM32CubeIDE will now look
like:
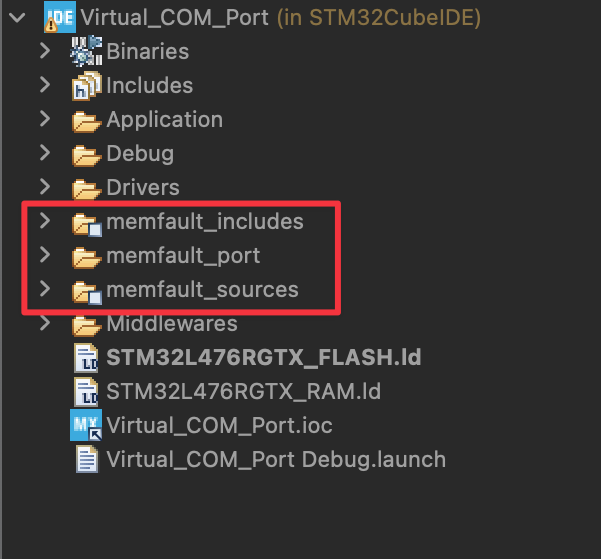
Create Platform-Specific Files
-
Create a folder to hold your platform-specific files and copy templates:
cd $PROJECT_ROOT
mkdir STM32CubeIDE/memfault_port
cp memfault-firmware-sdk/ports/templates/* $PROJECT_ROOT/STM32CubeIDE/memfault_port -
Link the RAM-backed coredump implementation in
$PROJECT_ROOT/memfault-firmware-sdk/ports/panics/src/memfault_platform_ram_backed_coredump.cinto$PROJECT_ROOT/STM32CubeIDE/memfault_port/. Dragging and dropping from the file system is easiest. Select the Link to files option after dropping the file into thememfault_portfolder: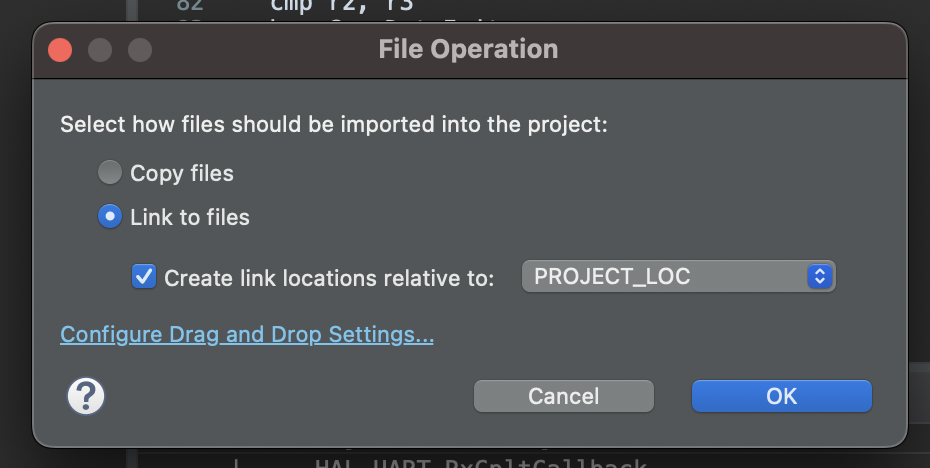
Details
Alternatively, sources can be explicitly linked via the Import wizard. Right click in the
memfault_portand select Import. Then, select the File System import option: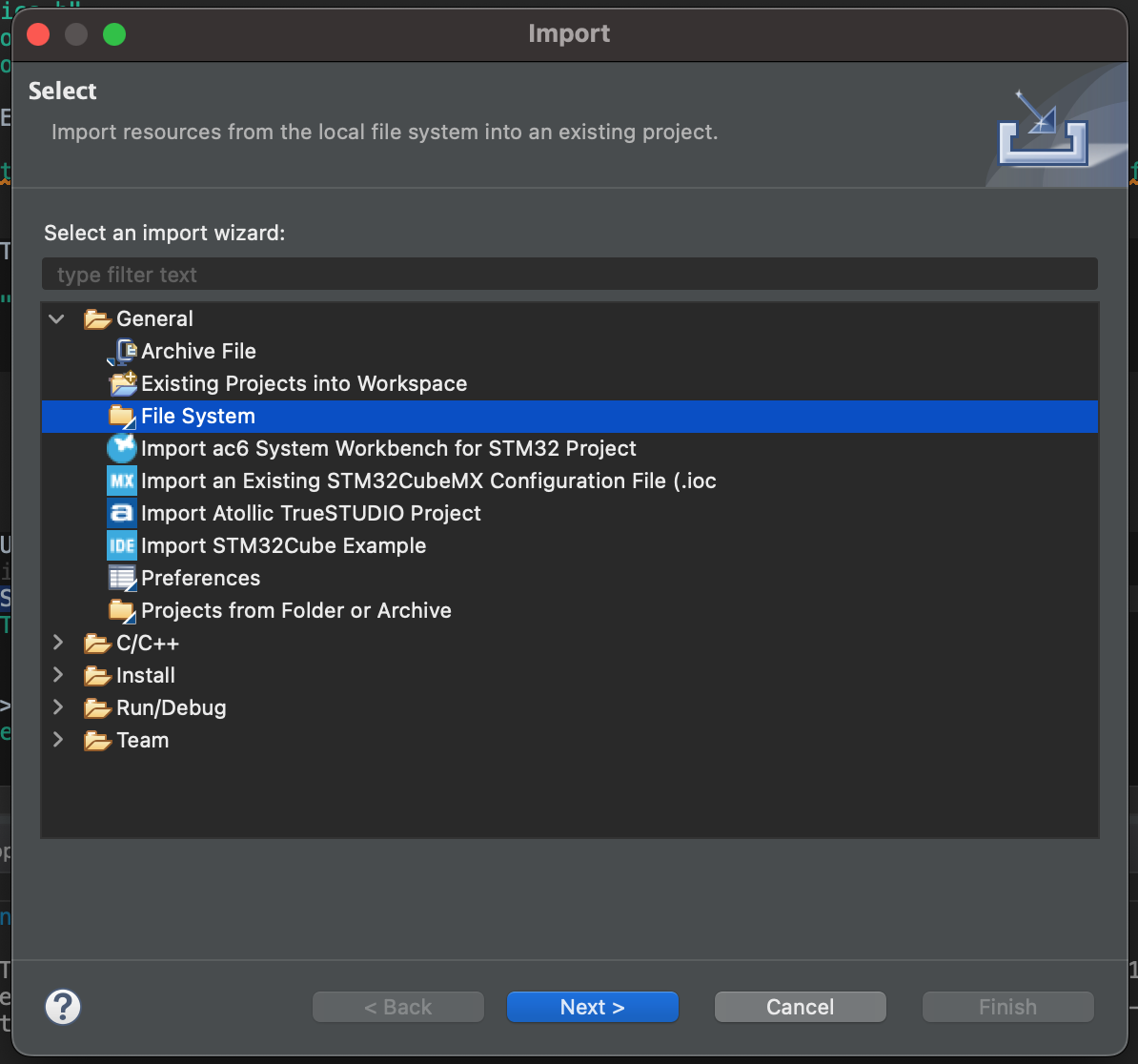
Choose s
$PROJECT_ROOT/memfault-firmware-sdk/ports/panics/src/memfault_platform_ram_backed_coredump.cfrom the file system, and choose to link in the workspace: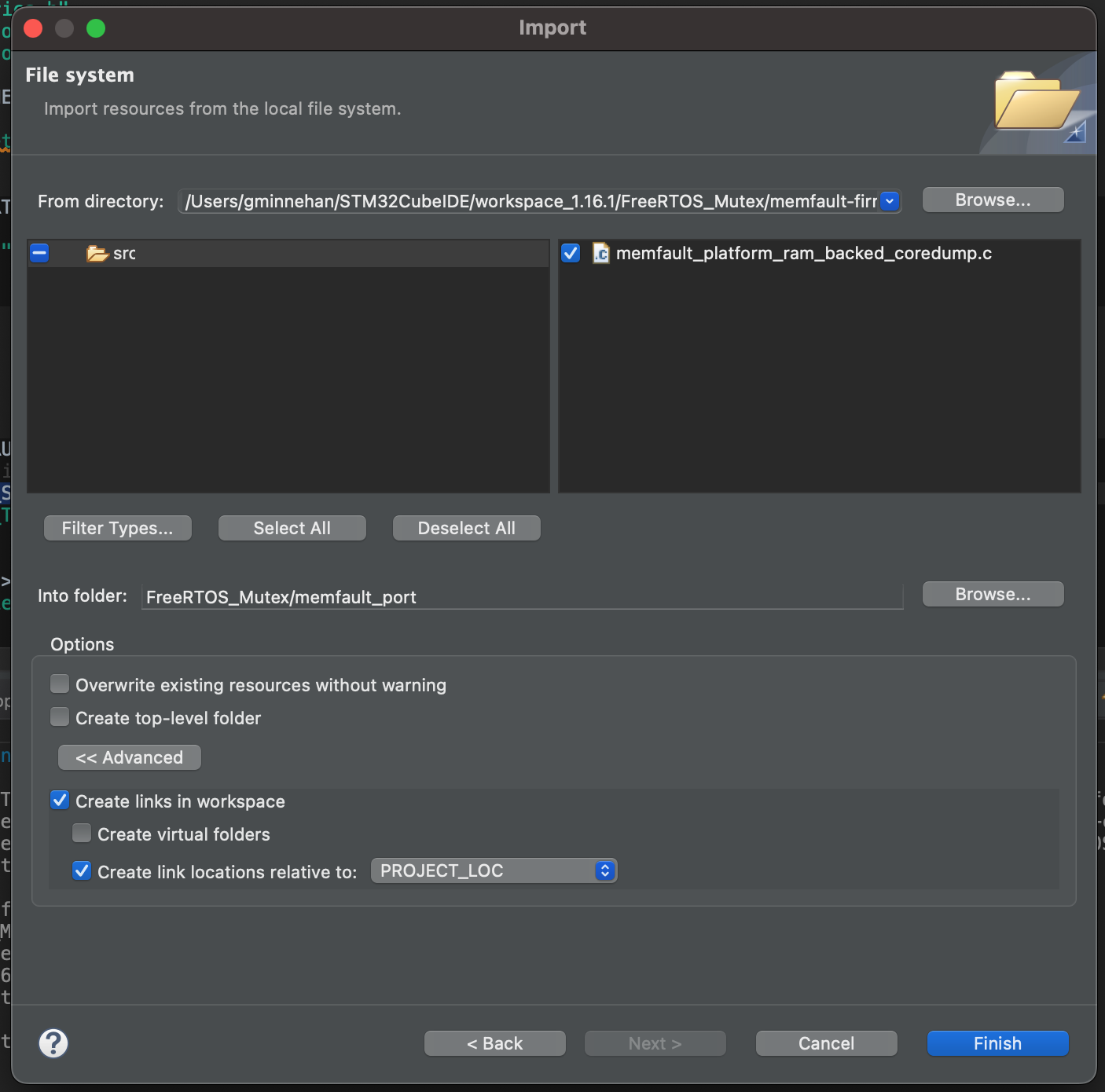
If prompted, do not overwrite the
memfault_portfolder. When finished, yourmemfault_portfolder in STMCubeIDE will look like:
-
Add this new
memfault_portfolder to the project include paths under Properties > C/C++ Build > Settings > Tool Settings > MCU GCC Compiler > Include Paths. Be sure this setting is applied to "All configurations".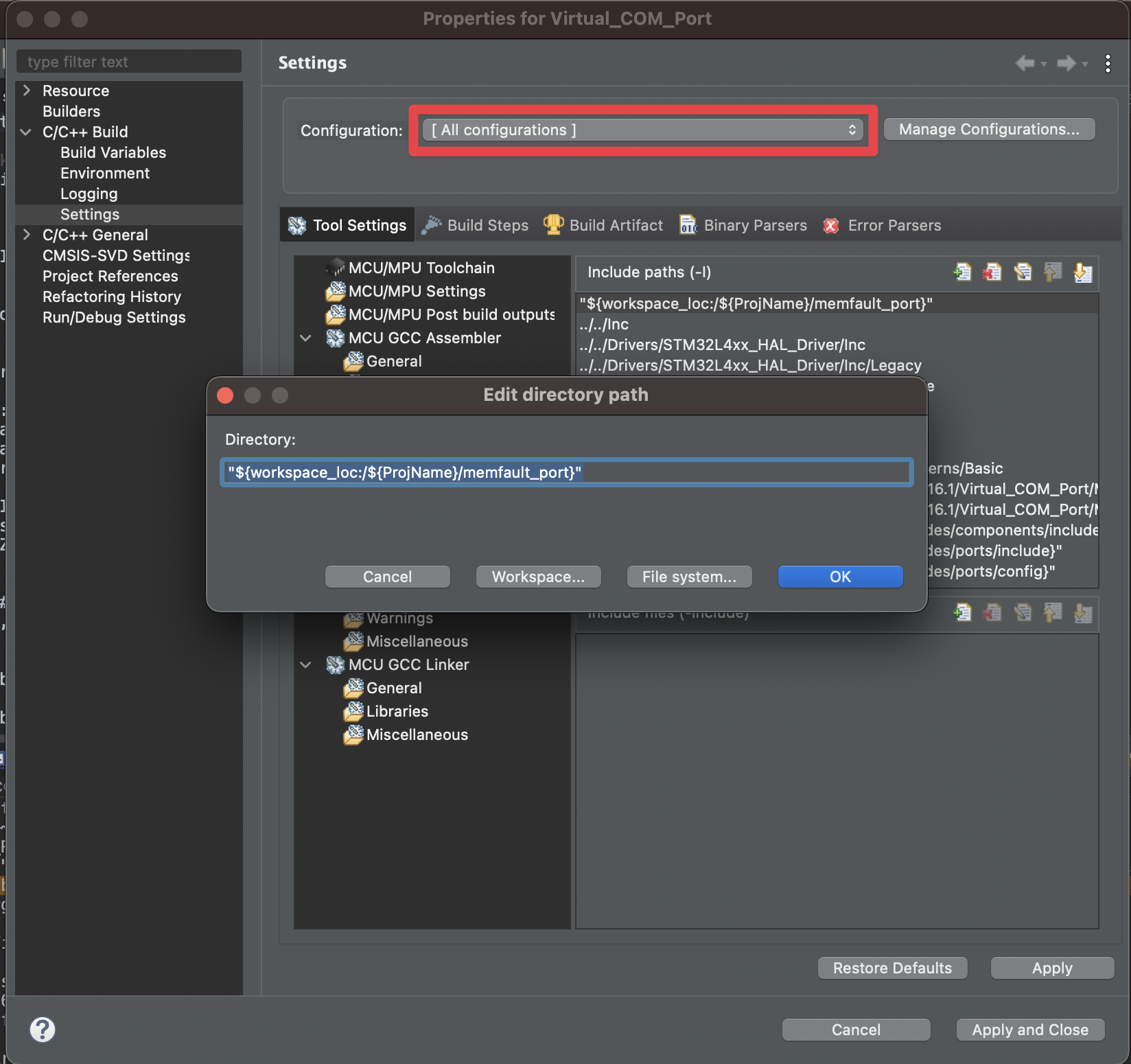
-
Add the required macro option in
memfault_port/memfault_platform_config.h:memfault_platform_config.h#define MEMFAULT_USE_GNU_BUILD_ID 1Right after the
.textsection in your linker file, add the_start_gnu_build_id_start. For this sample project, we editSTM32L476RGTX_FLASH.ld:.note.gnu.build-id :
{
__start_gnu_build_id_start = .;
KEEP(*(.note.gnu.build-id))
} > FLASHinfoBe sure to update
FLASHto match the name of the section.textis placed in!
Remove Conflicting Exception Headers
Memfault provides exception handlers to capture crashes properly. STM32 provides these handlers by default, and a linker error such as the following will be emitted when left in:
~/STM32CubeIDE/workspace_1.16.1/Virtual_COM_Port/memfault-firmware-sdk/components/panics/src/memfault_fault_handling_arm.c:433: multiple definition of `NMI_Handler'; ./Application/User/stm32l4xx_it.o:~/STM32CubeIDE/workspace_1.16.1/Virtual_COM_Port/Src/stm32l4xx_it.c:89: first defined here
Remove, rename, or weakly define the handler definitions for the following
handlers provided by STM32 to allow Memfault's to be used. For this sample
project, they are defined in stm32l4xx_it.c:
NMI_Handler()HardFault_Handler()MemManage_Handler()BusFault_Handler()UsageFault_Handler()
Boot Memfault & Enable Basic Platform Logging
-
Add the Memfault platform boot function to your
main()function after your UART console has been initialized. For example:main.c/* Private includes ----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
#include "memfault/components.h"
/* USER CODE END Includes */
// ...
int main(void)
{
// ...
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
memfault_platform_boot();
/* USER CODE END 2 */
// ...
}; -
Memfault prints a few log messages when this function is called. Add a simple definition to
memfault_port/memfault_platform_log_config.hto push these prints to the console. For example:memfault_port/memfault_platform_log_config.h#include <stdio.h>
#define _LOG_IMPL(lvl, fmt, ...) \
do { \
printf(fmt "\r\n", ## __VA_ARGS__ ); \
} while (0)
#define MEMFAULT_LOG_DEBUG(fmt, ...) _LOG_IMPL(kMemfaultPlatformLogLevel_Debug, fmt, ## __VA_ARGS__)
#define MEMFAULT_LOG_INFO(fmt, ...) _LOG_IMPL(kMemfaultPlatformLogLevel_Info, fmt, ## __VA_ARGS__)
#define MEMFAULT_LOG_WARN(fmt, ...) _LOG_IMPL(kMemfaultPlatformLogLevel_Warning, fmt, ## __VA_ARGS__)
#define MEMFAULT_LOG_ERROR(fmt, ...) _LOG_IMPL(kMemfaultPlatformLogLevel_Error, fmt, ## __VA_ARGS__)
#define MEMFAULT_LOG_RAW(fmt, ...) _LOG_IMPL(kMemfaultPlatformLogLevel_Debug, fmt "\n", ## __VA_ARGS__) -
Then, tell Memfault to pick up these sources by adding the following define in
memfault_port/memfault_platform_config.h:memfault_port/memfault_platform_config.h#define MEMFAULT_PLATFORM_HAS_LOG_CONFIG 1
✅ Build Check
Build the project to ensure the source was included correctly. After flashing your device, the following should appear on boot!
GNU Build ID: <build id>
S/N: DEMOSERIAL
SW type: app-fw
SW version: 1.0.0
HW version: dvt1
Memfault Initialized!
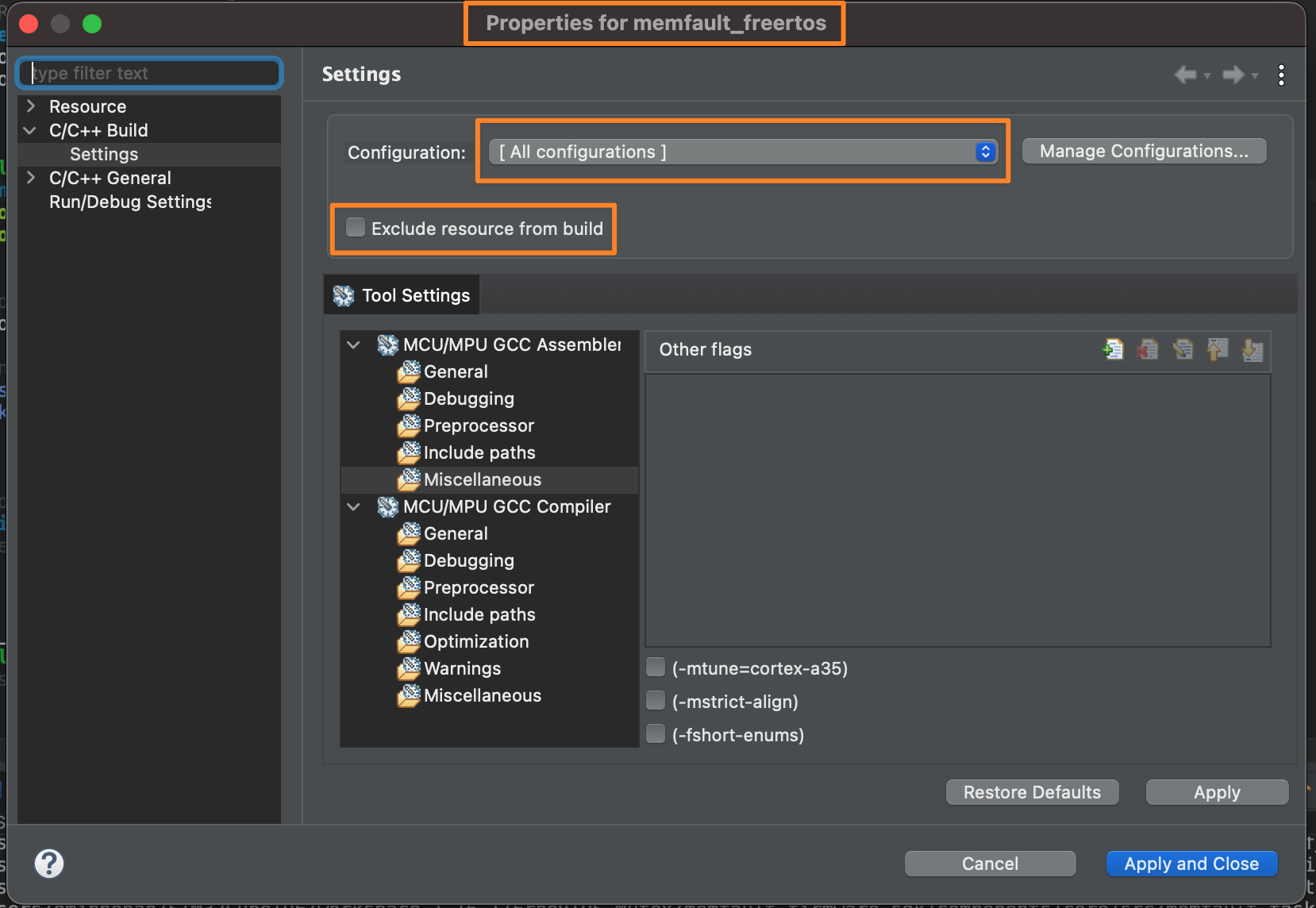
If you get undefined reference errors, confirm that the new folders
memfault_components and memfault_port are not excluded from the build. You
can verify this by right-clicking each folder and navigating to Properties.
Uncheck the Exclude resource from build box:
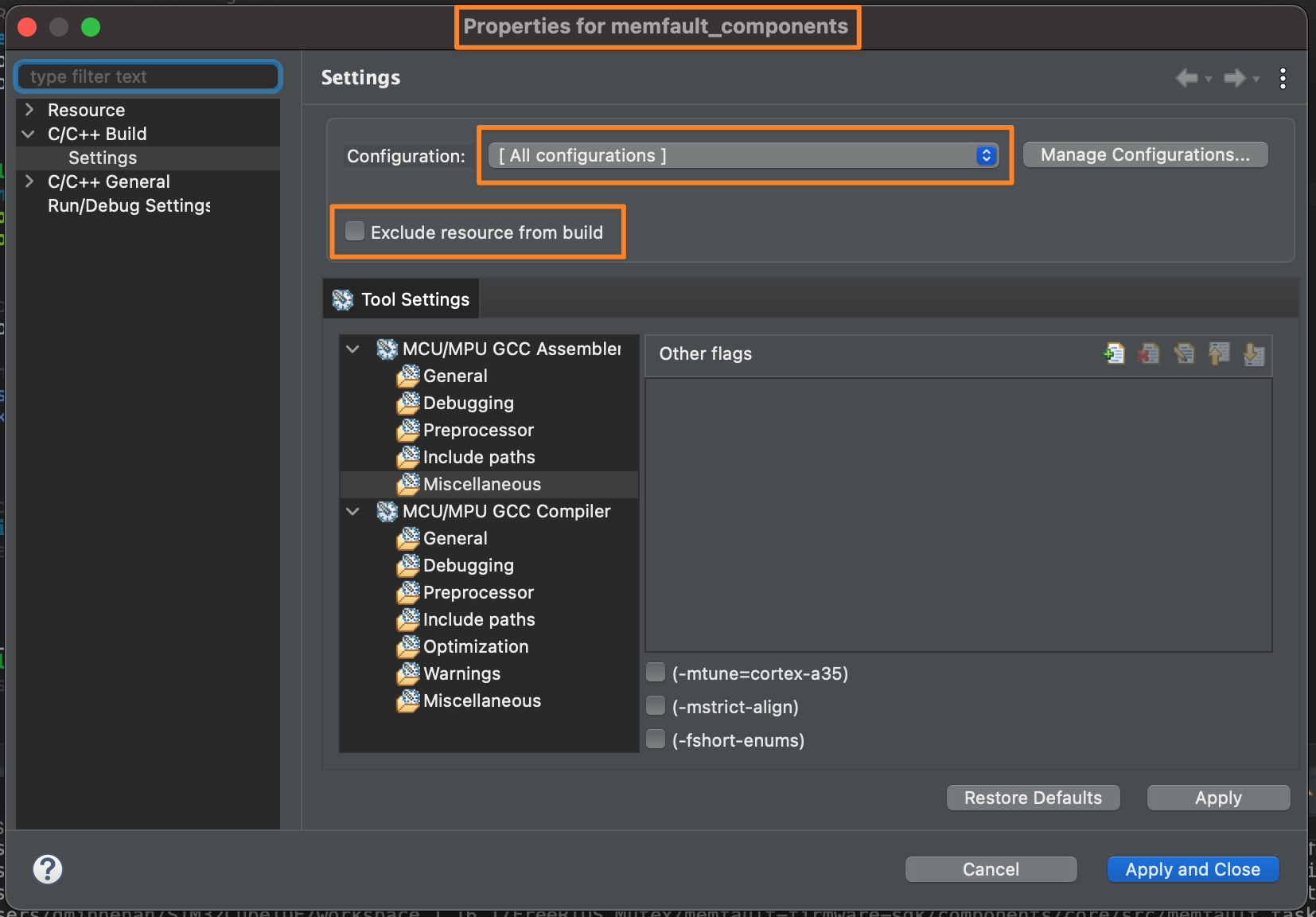
Be sure to apply this setting to "All configurations"!
3. Add STM32 Reboot Tracking
For the STM32 F4, F7, H7, L4, U5, and WB part families, ports are available for
recovering reset reason information by reading the "Reset and Clock Control"
(RCC)'s "control & status register" (CSR). See the
STM32Cube port folder in the Memfault Firmware SDK
for the correct file path to use below for including the reboot tracking
implementation. For this guide, we will use the l4 port:
- Add
memfault-firmware-sdk/ports/stm32cube/l4/rcc_reboot_tracking.c
memfault_componentsvia the drag and drop method described earlier. - Remove definition for
memfault_reboot_reason_get()inmemfault_platform_port.c
✅ Build Check
Rebuild to ensure the new reboot tracking was adding correctly. A new print should appear on boot:
GNU Build ID: <build id>
S/N: DEMOSERIAL
SW type: app-fw
SW version: 1.0.0
HW version: dvt1
Reset Reason, RCC_CSR=0x1c000600
Reset Causes:
Software
Memfault Initialized!
4. (If applicable) Integrate FreeRTOS Port
-
Execute the eclipse patcher to include FreeRTOS port sources:
python3 memfault-firmware-sdk/scripts/eclipse_patch.py \
--memfault-sdk-dir memfault-firmware-sdk \
--project-dir STM32CubeIDE \
--target-port freertos -
Add link to the FreeRTOS port heartbeat config folder
memfault-firmware-sdk/ports/freertos/configinsidememfault_includes/ports. Drag and drop this config folder and select Link to files and folders: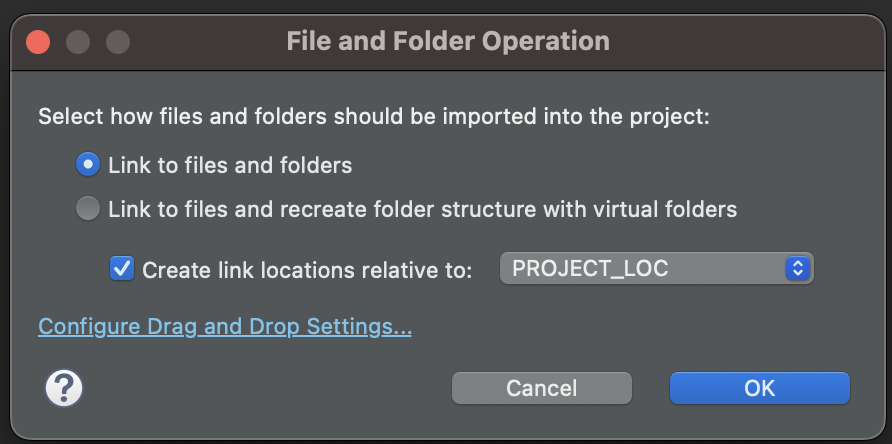
The
memfault_includesfolder should now look like: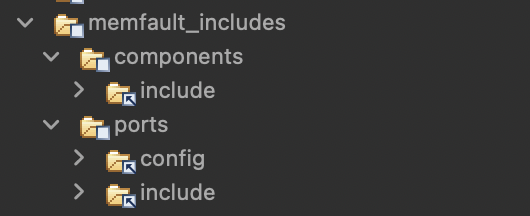
-
Add an include path to
memfault_includes/ports/configfolder in project settings. Be sure to apply this setting to "All configurations". -
Add
#include "memfault_metrics_heartbeat_freertos_config.def"to yourmemfault_port/memfault_metrics_heartbeat_config.def -
Remove definition for
memfault_platform_metrics_timer_boot()inmemfault_platform_port.c. This is implemented by the FreeRTOS port in the SDK. -
Remove definition for
vApplicationStackOverflowHook()— the Memfault FreeRTOS port provides a definition for this as well. -
Add the following to your
memfault_platform_port.c:-
Add
#include "memfault/ports/freertos.h" -
Add
memfault_freertos_port_boot()to the beginning of yourmemfault_platform_boot():memfault_platform_port.c#include "memfault/components.h"
#include "memfault/ports/freertos.h"
int memfault_platform_boot(void) {
// Initialize the FreeRTOS port
memfault_freertos_port_boot();
MEMFAULT_LOG_INFO("Memfault FreeRTOS Port Initialized!");
memfault_build_info_dump();
memfault_device_info_dump();
memfault_platform_reboot_tracking_boot();
// ...
return 0
}
-
-
Follow the instructions on the RTOS Analysis page to capture the necessary RTOS variables for thread decode in coredumps
✅ Build Check
Rebuild to ensure the new FreeRTOS source was added properly. After flashing, verify the new print on boot!
GNU Build ID: <build id>
S/N: DEMOSERIAL
SW type: app-fw
SW version: 1.0.0
HW version: dvt1
Reset Reason, RCC_CSR=0x1c000600
Reset Causes:
Software
Memfault Initialized!
Memfault FreeRTOS Port Initialized!
Testing Things Out
For testing the integration, Memfault recommends enabling Memfault's demo CLI on the target device.
Once enabled, you can try collecting a crash as a first step:
mflt> test_assert
The device will crash and reset. Once the CLI is back up, check that a coredump is available:
mflt> get_core
MFLT: [INFO] Has coredump with size: 20224
Dump the captured data to the console:
mflt> export
Copy the logs from the console, navigate to the "Integration Hub / Chunks Debug" view for your project, and paste the logs:
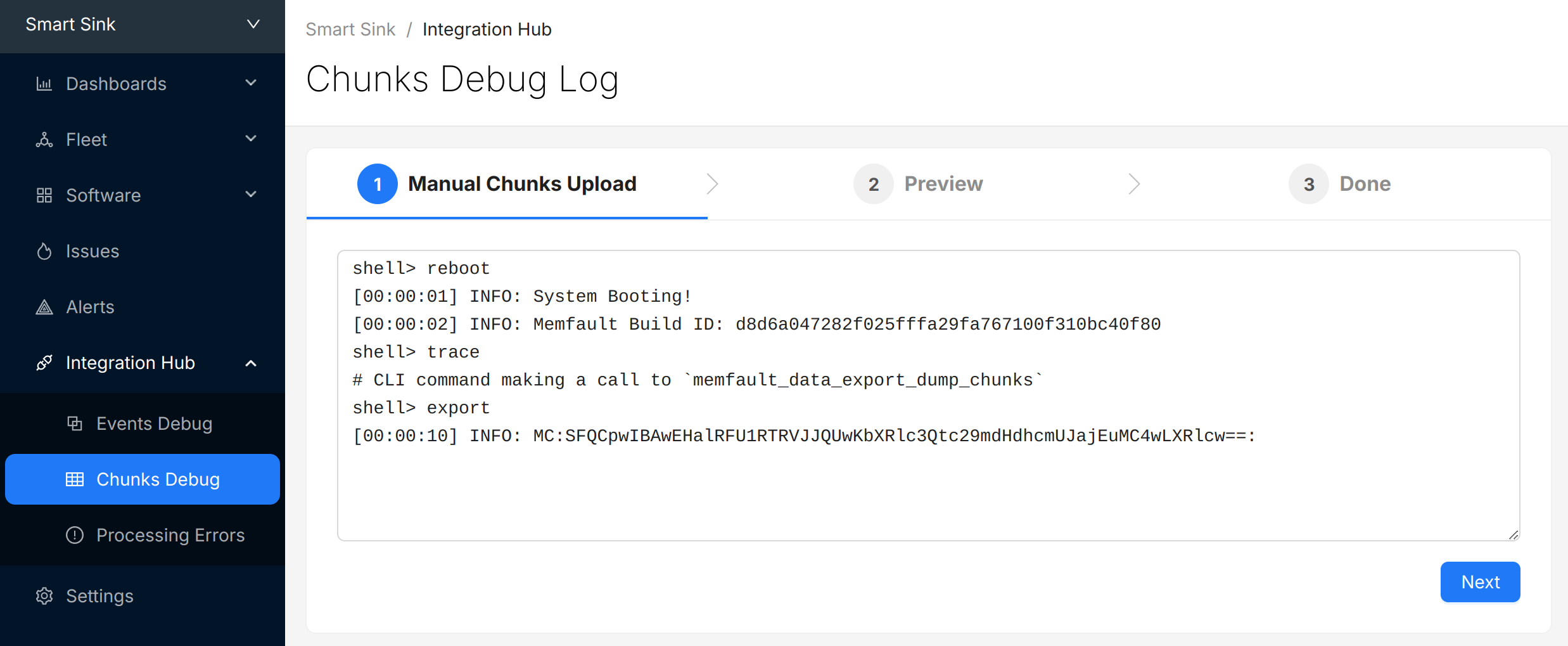
Testing Data Uploaded to Memfault
Now it's time to see data decoded in the Memfault platform. To do that, we first
need to upload the generated symbol file (for STM32CubeIDE projects, it's
usually $PROJECT_ROOT/STM32CubeIDE/Debug/<your project name>.elf or
$PROJECT_ROOT/STM32CubeIDE/Release/<your project name>.elf).
Upload Symbol File
At this point, you should be able to generate test events and crashes and push the data to the Memfault UI.
You can confirm the error traces and crashes have arrived successfully by navigating to the "Issues" page- there should be a new issue with the "Symbols Missing" label:
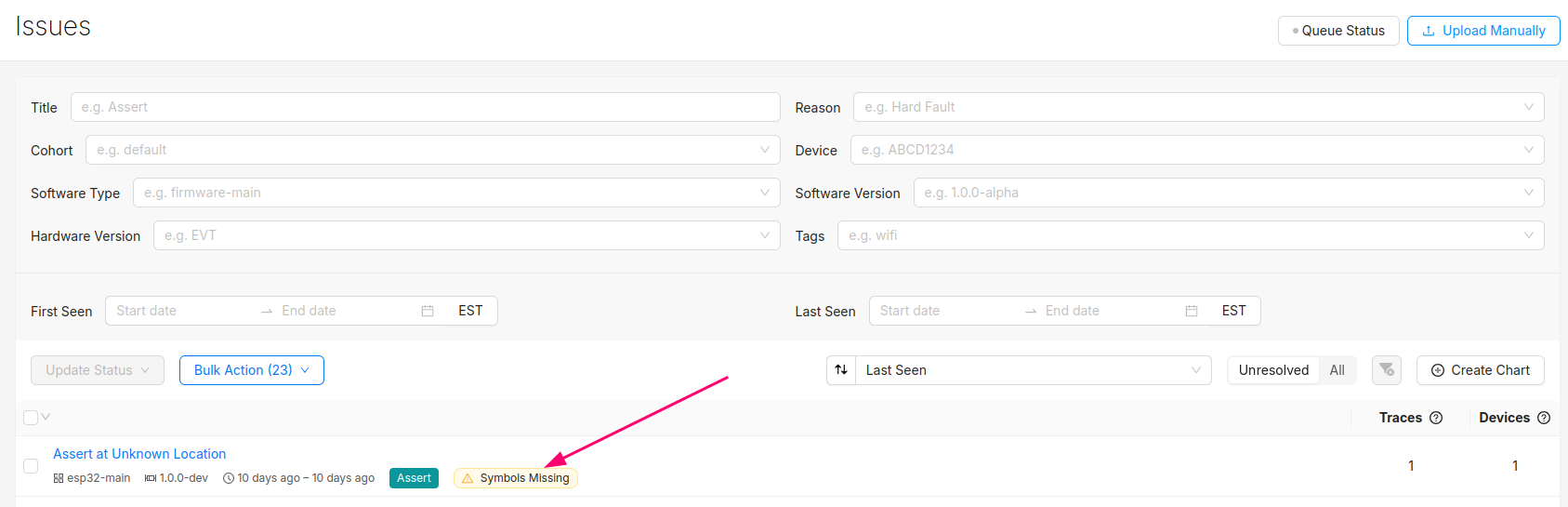
Clicking into the Issue will show the trace and a message that the symbol file is missing. It can be uploaded by clicking the button highlighted below:
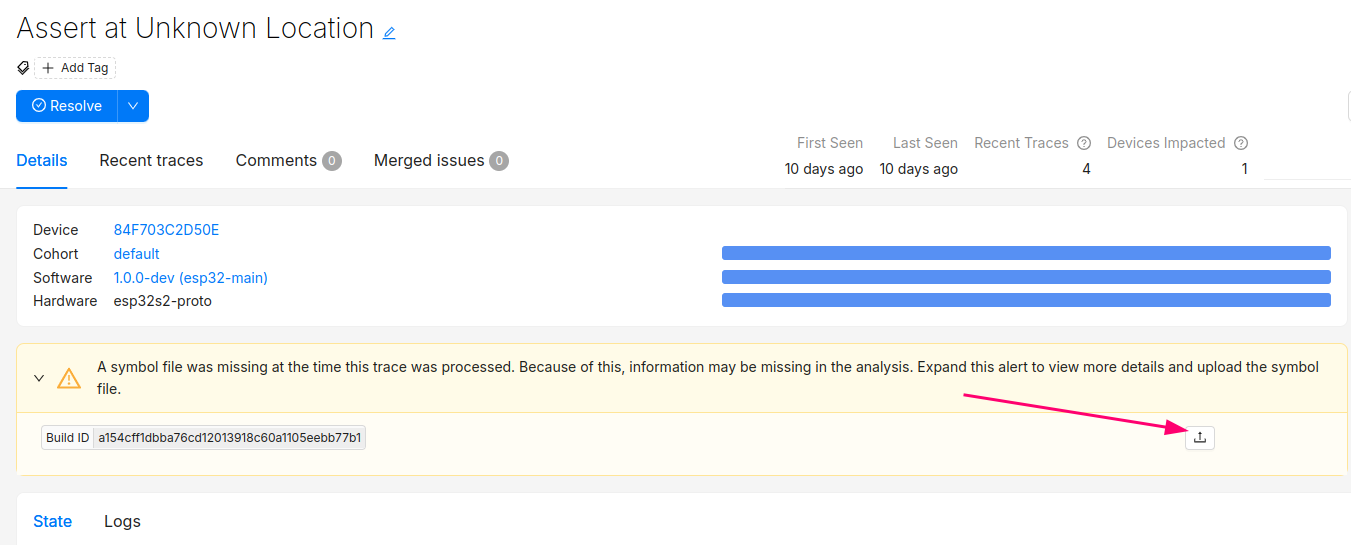
After this step, you will see the processed trace in the list of issues!
The Issue created when the symbol file is missing can now be set to resolved. It's good practice to always upload a symbol file before devices send any data.
Symbol files can also be uploaded from the Software → Symbol Files tab (follow this deep link to be brought to the symbol file upload point in the UI):
In addition to supporting decoding trace/coredump data, symbol files are also required for decoding Metrics.
You can programmatically upload symbol files with the Memfault CLI tool.
Symbol files should be uploaded to Memfault before devices send any data, to ensure all device data can be decoded.
Next Steps
For more information on logging, OTA, reboot reasons, and other pieces of Memfault, explore the Core Subsystems Guides!