Android SDK Configuration
The purpose of the Memfault Android SDK [source] is to make it easy to automatically collect detailed diagnostics from your entire Android device, from low-level or hardware issues to high-level application crashes, and upload them automatically to Memfault for processing and visualization.
This document details ways to configure the SDK.
For a detailed guide on how to integrate the SDK into your devices, see the Getting Started guide.
SDK Collection Systems
The Android SDK supports two data collection systems:
- Bug reports, a diagnostics reporting tool built into AOSP.
- Caliper, a system designed to precisely specify what diagnostics information to collect on the device for improved performance and privacy.
We do not recommend collecting Bug Reports from production devices, because of the collection overhead, upload size, and privacy implications.
By default, periodic Bug Report collection is disabled, and all Caliper data collection is enabled. This can be configured in the Memfault dashboard - see Configuration.
Memfault Caliper
Memfault's Caliper system can be used to precisely specify what diagnostics information to collect on the device. We recommend using this system because it allows for:
- The smallest possible runtime footprint on the device
- Minimal bandwidth and on-device storage
- Fine-grained control over what data and when it's collected
Caliper uses the DropBoxManager API to receive traces and crash data from the operating system.
Metrics are collected using the Batterystats subsystem, and by individually querying AOSP services reactively and periodically.
Logs are collected from logcat. See Logging.
| Bug Reports | Caliper | |
|---|---|---|
| Collection mechanism | Pull: collects all system state, metrics & logs at a point in time. Events/metrics may be missed if they occur long enough ago. | Event-driven: collects crashes as they occur using DropBoxManager, periodically collecting logs and metrics. |
| Performance Impact | Collecting a bugreport (using dumpstate) is CPU-intensive, and can have a noticeable impact (causing stuttering/lag on the device). | Caliper collects small chunks of relevant information on a regular basis, with low impact. |
| Size | Bug Reports can be huge files - this is not configurable. Much of what is collected is not useful (e.g. every dumpsys, unfiltered logs). | Caliper only collects useful data - so storage/upload sizes are much smaller. This is entirely remotely configurable (collection intervals, log filters, which types of crashes to collect, etc). |
| Privacy | PII may be contained within a Bug Report (e.g. email addresses in logs, or IP addresses in dumpsys output). | Logs can be scrubbed for PII on-device before upload. What data is collected is fully configurable. |
| Logs | Logs are collected at the time of taking the Bug Report. Server-side Log Scrubbing is available. | Logs (from all buffers) are collected at a regular interval, and uploaded when a crash occurs. They are scrubbed on-device for PII. |
| Crashes | Crashes are parsed from logs (may be missed if buffers expire). | Crashes are processed as they occur, via DropBoxManager. Kernel oops are extracted from regular logcat collection. |
| Reboots | N/A | Collected on boot, and visible on timeline/fleet overview pages. |
| Battery Metrics | Battery metrics are collected, and displayed on the Bug Report tab. They are not available as fleet-aggregated metrics. | Battery metrics are collected and displayed continuously on the Device Timeline tab. They are also available as fleet-aggregated timeseries metrics. |
| Installed Apps | Installed app versions can be viewed on the Bug Report tab. They cannot be used as Device Properties/in Device Search. | Installed app versions are collected as Device Properties. These can be used for Device Search (or to create Device Sets). |
| System Properties | Can be viewed on the Bug Report tab. They cannot be used as Device Properties/in Device Search. | Are collected as Device Properties. These can be used for Device Search (or to create Device Sets). |
| Built-In Metrics | N/A | Caliper collects device storage/temperature metrics (more metrics will be added here in the future). These can be used as fleet-wide timeseries metrics for charting/device search. |
| Configurability | We provide an AOSP patch to optionally enable dumpstate minimal mode - but exactly what this collects is not remotely configurable. | Fully configurable on the Memfault dashboard. Settings are synced down to devices, including enabling/disabling each type of data, configuring log filters and scrubbing rules, and tuning collection intervals. |
See the Changelog for a complete history of when features were added to the SDK.
Installation Configuration
Enabling the SDK at Runtime
By default, the SDK assumes it is running on a device that may contain Personally Identifiable Information (PII). As such, it will not run until it is explicitly told to do so (e.g. when user consent has been obtained). Once enabled, that value will be persisted in preferences. If the Bort app's data is cleared, this value must be set again.
To enable the SDK, send an intent to the ControlReceiver. Note that the sender
must hold the permission specified in the BORT_CONTROL_PERMISSION property
in bort.properties. The default is com.memfault.bort.permission.CONTROL,
which may only be may only be granted to applications signed with the same
signing key as MemfaultBort (signature) or applications that are installed
as privileged apps on the system image (privileged). See
Android protectionLevel
for further documentation.
Intent("com.memfault.intent.action.BORT_ENABLE").apply {
component = ComponentName(
APPLICATION_ID_BORT, // Whatever you have chosen for the application ID
"com.memfault.bort.receivers.ControlReceiver"
)
putExtra("com.memfault.intent.extra.BORT_ENABLED", true)
}.also {
context.sendBroadcast(it)
}
To disable the SDK, for example if the user later revokes consent, simply send the same intent with the opposite boolean extra
Intent("com.memfault.intent.action.BORT_ENABLE").apply {
component = ComponentName(
APPLICATION_ID_BORT,
"com.memfault.bort.receivers.ControlReceiver"
)
putExtra("com.memfault.intent.extra.BORT_ENABLED", false) // <-- Now disabled
}.also {
context.sendBroadcast(it)
}
If the SDK is running on a device that does not require user consent, this
requirement can be disabled by changing a property in bort.properties:
RUNTIME_ENABLE_REQUIRED=false
If you wish to enable the SDK on a development device over ADB, bort_cli.py
provides a convenience command:
./bort_cli.py enable-bort --bort-app-id your.app.id
The enable-bort command runs this ADB command under the hood:
adb shell am broadcast --receiver-include-background \
-a com.memfault.intent.action.BORT_ENABLE \
-n your.app.id/com.memfault.bort.receivers.ShellControlReceiver \
--ez com.memfault.intent.extra.BORT_ENABLED true
Setting Project Key at Runtime
A Project Key is required at compilation time of the Bort APK, but it can also
be changed at runtime if needed. This can be useful for moving test devices to a
separate project so their metrics and issues don't pollute the main project
being used. To use this feature, add ALLOW_PROJECT_KEY_CHANGE=true to your
bort.properties.
There are two ways to change the Project Key: using a sysprop or using an Intent.
Use either a sysprop or an Intent to change the Project Key, but never both. If a sysprop is configured at build time, then a broadcast cannot be used.
Intent
This is supported from Android SDK 4.5.0 onwards.
Once enabled in bort.properties, you can run the following adb command to
change the key.
adb shell am broadcast \
-a com.memfault.intent.action.UPDATE_PROJECT_KEY
-n com.memfault.smartfridge.bort/com.memfault.bort.receivers.ShellControlReceiver
--es com.memfault.intent.extra.PROJECT_KEY "your_new_project_key"
This can be called before the SDK is enabled at runtime, which will ensure that the Project Key compiled into the apk will never be used.
Excluding the com.memfault.intent.extra.PROJECT_KEY parameter will reset to
the key compiled into the APK (from Android SDK 4.6.0).
Make sure that the PROJECT_KEY_SYSPROP gradle property is empty, if you intend
to change the Project Key using an Intent.
Sysprop
This is supported from Android SDK 4.11.0 onwards.
In addition to ALLOW_PROJECT_KEY_CHANGE=true, a sysprop key must be configured
in bort.properties. If your Project Key is defined in the a.b.c.project_key
system property, then set PROJECT_KEY_SYSPROP=a.b.c.project_key.
If PROJECT_KEY_SYSPROP is configured, then the Android SDK will check that
sysprop every time the main Bort app starts. If the sysprop is set, then this
will be used as the Project Key. If the sysprop is not set (or is empty) then
the key compiled into the APK will be used.
If the sysprop value is changed after device boot, then be sure to kill the Bort app, so that it will read the new value when it next starts.
Changing the Project Key using either mechanism will delete all pending MAR files queued to be uploaded.
Software Versions, Hardware Versions and Device Serials
It is possible to customize which values to use as the Software Version, Hardware Version or Device Serial for a given project. For background on software and Hardware Versions, see Software and Hardware Versions.
The customization is done during the project creation. To change these settings, you must create a new project.
The Android SDK automatically retrieves these settings during the APK build process so no additional configuration is required.
Install the SDK to an alternate location
The default SDK location is in vendor/memfault/bort. If you would prefer to
place the SDK at a different location in your source tree, first clone the SDK
to the desired location in the source tree, then find and replace instances of
vendor/memfault/bort with your target directory.
For example, to place the SDK in the system partition, clone the SDK to
packages/apps/bort then run find and replace (e.g. on BSD/macOS):
LC_ALL=c find . \( -type d -name .git -prune \) -o -type f -exec sed -i '' "s/vendor\/memfault\/bort/packages\/apps\/bort/g" {} +
SDK Settings Configuration
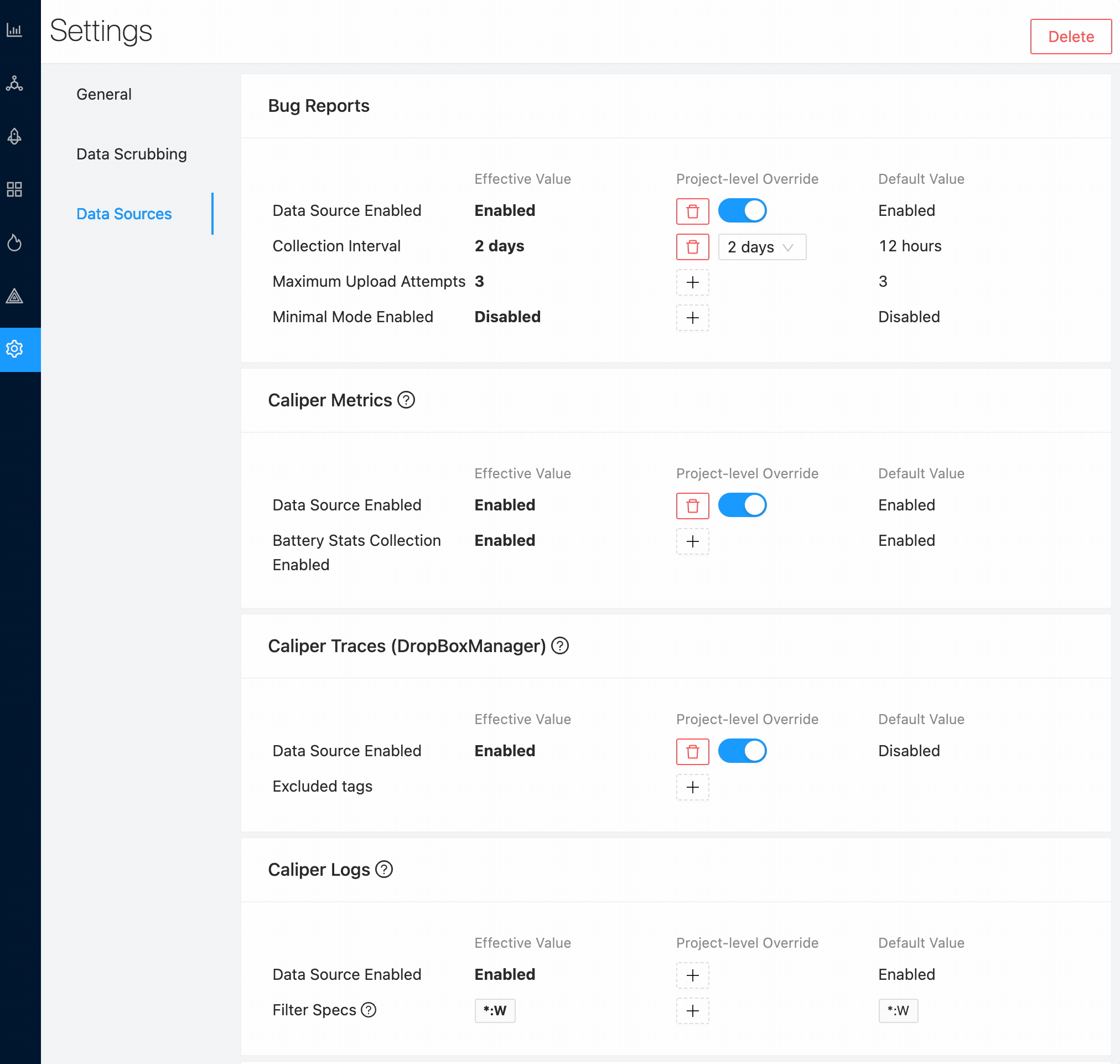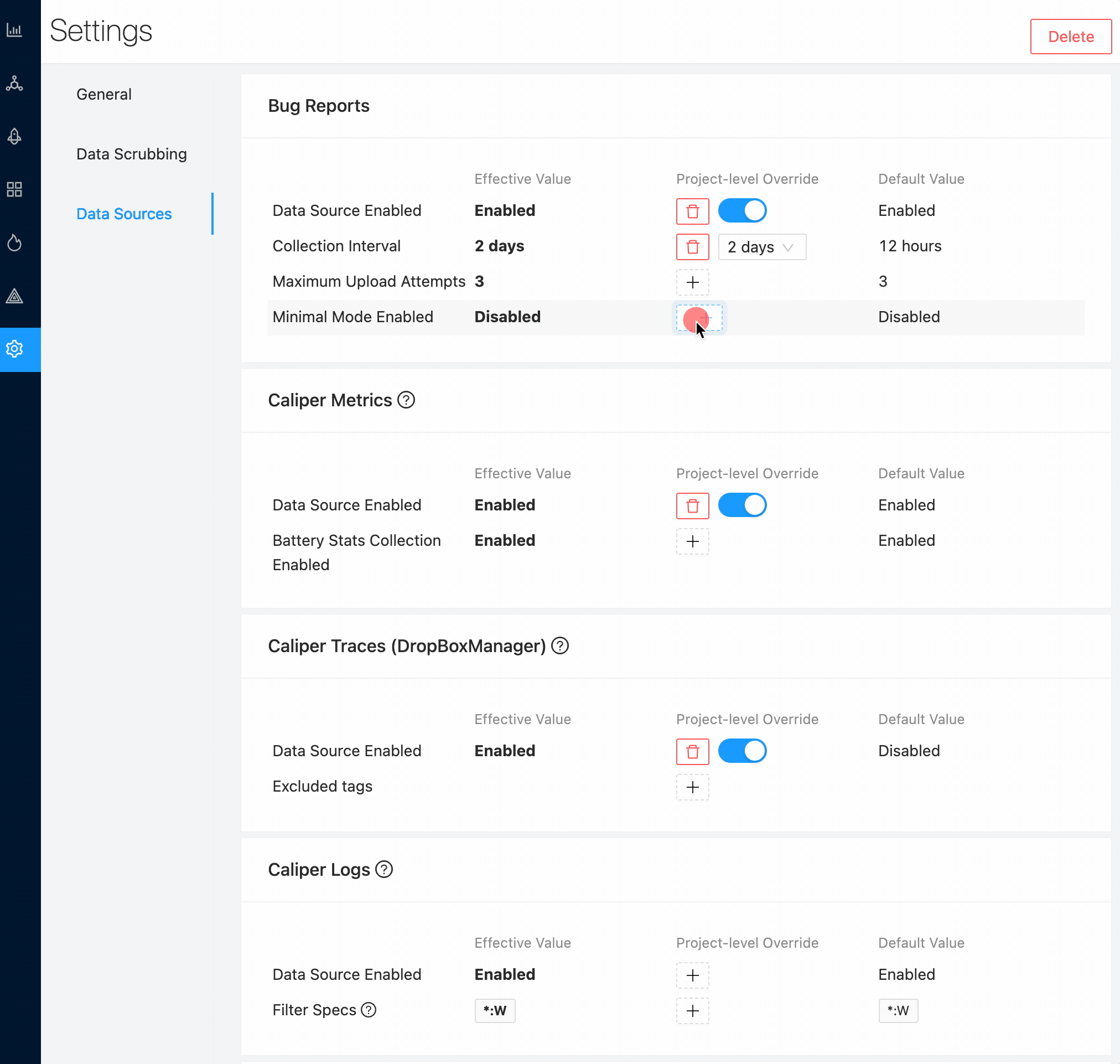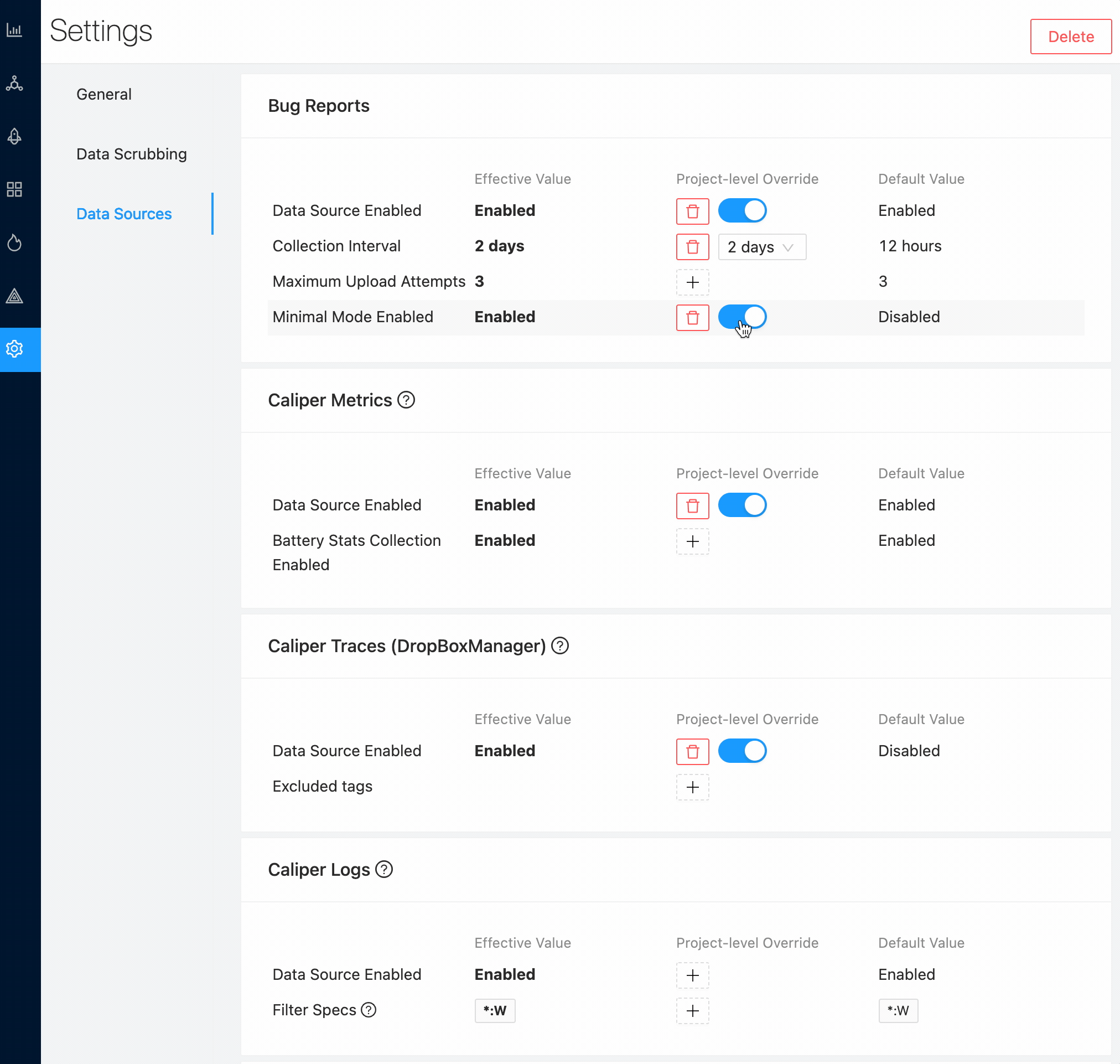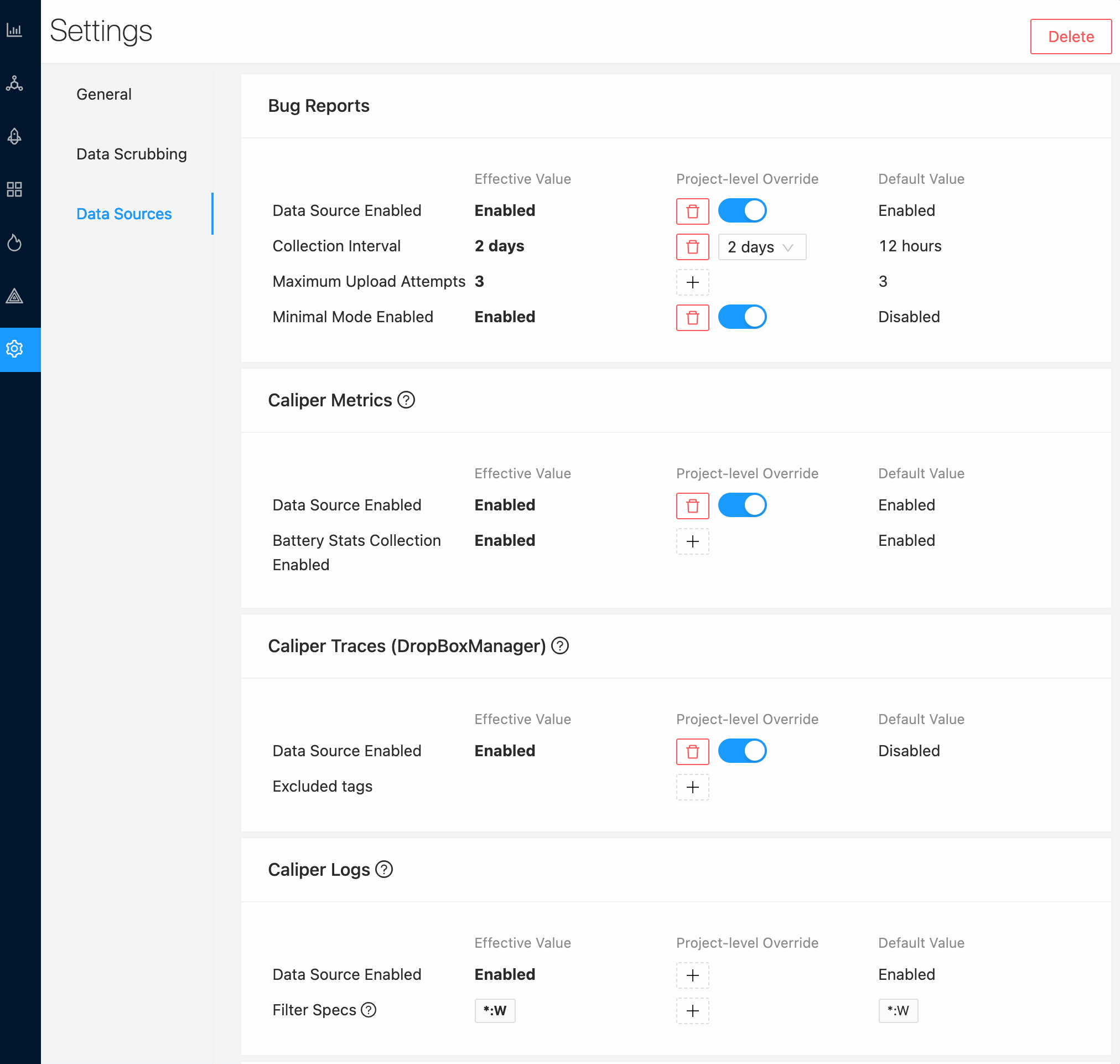
The Android SDK contains an Over The Air settings system so that settings are defined on the web in your Memfault project, and the SDK will periodically pull the latest settings at run-time. This makes it easy to enable or disable different data sources, or change configuration options. Settings can be updated through the web UI or programmatically via a web endpoint -- no need to deploy an app or OS update.
The settings can be found in the Settings part of the web UI. SDK settings are
only visible to and configurable by Project Managers and
Organization Admins.
Ingestion of data from the Android SDK may be rate-limited. We do not recommend lowering the collection intervals to be less than the default values.
Fallback SDK Settings
As part of the build process, the Android SDK will fetch the current SDK
settings and store them as a file called settings.json. We recommend storing
this file in your version control system. The Android SDK embeds this file as
fallback SDK settings, used temporarily until fresh settings are retrieved from
the web, at run-time.
If, during the build process, the Android SDK detects the local settings.json
is stale, the build will intentionally fail to alert you that the default
settings are out of date. To fix this, remove the stale settings.json file and
re-run the build.
If you wish to disable this check, you can skip this step when building the Bort APK by setting a gradle property:
SKIP_DOWNLOAD_SYSTEM_SETTINGS_JSON=1
Data Reporting Frequency
There are two modes in which the Bort app can be configured to send data. The first is by bundling all data into a MAR (Memfault Archive) file, or by sending each piece of data individually to Memfault as it's collected from the system (deprecated - see below).
During development, you will want to increase the frequency at which data is sent. To do this, enable Developer Mode
Uploading MAR files
When uploading data via MAR files, the Bort app collects diagnostic data for 2 hours and then bundles it all together in a single MAR file and uploads it.
Depending on the time at which data was collected from the system, it may take up to 2 hours for it to be sent to Memfault.
The use of MAR files is required to use Memfault's Fleet Sampling feature.
Uploading individual files
This method of uploading files from the Android SDK is deprecated as of Android SDK 4.1, and was completely removed in Android SDK 4.6.0.
This configuration would upload individual files to Memfault. After the data is collected from the system, it is uploaded up to 15 minutes later.
Sync Behavior and Triggers
Memfault uses the Android JobScheduler APIs to schedule its work following Android's best practices. To modify this behavior for your project see the following options.
Reducing Data on Metered Networks
Two Project settings control if data sent when on a metered network. The "Allow Uploads on Metered Networks" and "Allow OTA downloads on Metered Networks" settings available in your Project Settings - Data Sources configure Memfault to put either a NetworkType.CONNECTED (if true) or NetworkType.UNMETERED constraint on its network requests.
Sync Rates
Memfault splits sync data into two different categories, OTA releases and data contained in Memfault Archives (MAR). MAR data consists of metrics, logs, and DropBoxManager Entries collected by Memfault.
| Type | Default Rate |
|---|---|
| MAR Data | 2 hours |
| OTA Releases | 12 hours |
These settings can be adjusted if desired by contacting support.
Retries
OTA requests will retry linearly at 15m intervals (15m, 30m, 45m, ..).
All other requests will retry exponentially starting at 5m (5m, 10m, 20m, 40m, ..).